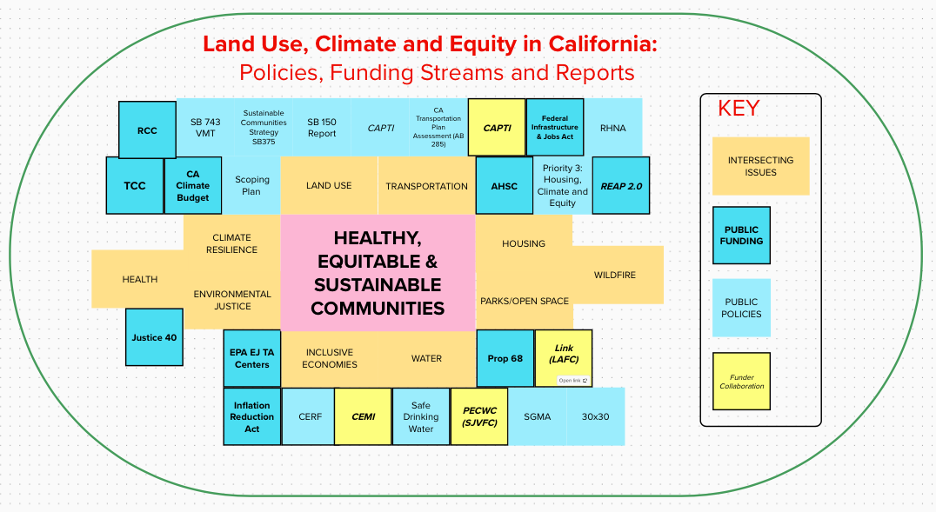
There’s always a lot going on in California, the most populated state in the nation by far, and one of the biggest economies in the world. Since its inception in 2009, Smart Growth California has worked at the intersection of issues related to land use, climate, and equity. This plays out in myriad ways across our state and as you can imagine, there’s a lot going on as it relates to housing, transportation, water, wildfires, parks, environmental justice, inclusive economies, health, climate resilience, and the built environment.
As we prepare for our Funder Summit in Sacramento (March 4-6, 2024), below is a short summary of intersecting policies, reports, and funding streams that we’ve discussed at Smart Growth California workgroup meetings over the years.
- Statewide Policies, Funding, and Key Reports
- SB 375 (SCS – Sustainable Communities Strategies): Smart Growth California was formed in response to this landmark legislation that directed regions across the state to develop Sustainable Communities Strategies to meet California’s ambitious greenhouse gas reduction goals through better alignment of transportation and land use.
- 2022 Progress Report (SCS – Sustainable Communities Strategies): This report, prepared by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) shows that while good plans have been made, more is needed to implement sustainable communities across the state. Alarmingly, vehicle miles traveled across the state continue to increase. Two additional reports by nonprofits build upon these findings: NextGen Policy’s California at a Crossroads report and NRDC’s California is Short-Changing Climate-Friendly Mobility.
- CAPTI (Climate Action Plan for Transportation Infrastructure): This plan, developed by the California Transportation Commission (CTC) directs state agencies to align transportation spending with the state’s climate goals. Yet, highways continue getting built and implementation is slow.
- Scoping Plan: This plan, prepared by California Air Resources Board (CARB), lays out the states multi-faceted strategy to meet its climate goals. With transportation accounting for more than 40% of the state emissions, the most recent scoping plan aims to Reduce Vehicle Miles Traveled (VMT) by 25% by 2030.
- SB 285 (CA Transportation Assessment Report): This report, prepared by California Air Resources Board (CARB), highlights the various ways in which the state is falling short on meeting its climate and equity goals with current auto-oriented transportation investments. It alsogf lists several recommendations towards a more climate-resilient, community-oriented transportation system.
- SB 743: Replaced traffic congestion with Vehicle Miles Traveled (VMT) as the new lens for assessing transportation impacts on the environment under the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA). Implementation of the law is still a struggle, but it’s still one of the best tools we have to reduce VMT.
- Priority 3 Housing, Climate, and Equity: This work plan, developed by the Strategic Growth Council, lays out a set of short-term, doable actions that state agencies can take to implement existing plans and funding streams in support of sustainable communities.
- CA Climate Budget (2022): California lawmakers have allocated historic amounts of funding for a broad range of climate-related initiatives. Funding that most relates to what Smart Growth California focuses on are the following:
- REAP 2.0 (Regional Early Action Program 2021): This funding, administered by the California Housing and Community Development Department, allocated $600M in funding for regions across the state to implement their Sustainable Communities Strategies, which has included building more affordable housing near transit and supporting active and public transportation.
- TCC (Transformative Climate Communities Program): This program, administered by the Strategic Growth Council has funded several place-based, multifaced climate investments that have supported affordable housing near transit, active transportation, active transportation, parks and open space, and more.
- AHSC (Affordable Housing & Sustainable Communities Program): This program, administered by the Strategic Growth Council, has funded numerous equitable, transit-oriented, affordable housing communities across the state.
- RCC (Regional Climate Collaboratives): This program, administered by the Strategic Growth Council, has provided technical assistance and support to networks across the state to better access public funding and resources for communities.
- CERF (Community Economic Resilience Fund): This program, administered by the Governor’s Office of Planning and Research (OPR), supports regions around the state to develop plans for inclusive, economically resilient places. A future second phase will allocate funding for implementation.
- Prop 68 (Parks and Water Bond Act of 2018): This bond, approved by voters across California, is funding a wide variety of parks throughout the state.
- RHNA(Regional Housing Needs Assessment) and Housing Elements: The recurring RHNA process, overseen by the Californfgvvia Housing and Community Development Department assesses housing needs while local governments develop Housing Elements, as part of their general plans to meet those needs.
- 30×30 (Nature Based Solutions): This commitment, made by the State of California, aims to protect or preserve 30 percent of lands for conservation.
- SGMA (Sustainable Groundwater Management Act): This act, passed by the legislature, started a process and system to better account for and manage groundwater in the state of California.
- SB 375 (SCS – Sustainable Communities Strategies): Smart Growth California was formed in response to this landmark legislation that directed regions across the state to develop Sustainable Communities Strategies to meet California’s ambitious greenhouse gas reduction goals through better alignment of transportation and land use.
- Federal Policies, Funding, and Key Reports
- Infrastructure and Jobs Act: Billions in spending for public transportation, clean drinking water, and other climate-resilient infrastructure.
- Inflation Reduction Act: Reduces pollution, improves clean transit, supports clean energy, strengthens climate resilience
- Justice 40 Initiative (see UCLA Luskin Report): Working to deliver 40% of the overall benefits of climate and clean energy investments to disadvantaged communities.
- Philanthropic Collaborations
- Opportunities for Philanthropic Investment: Funders active in Smart Growth California workgroups have discussed the unique role that philanthropy can play in supporting the equitable implementation of federal and state funding streams. There is more money “on the table” for equitable smart growth than in decades, and yet history has shown that simply having resources is not enough to ensure it gets to where it is needed most.
This is by no means an exhaustive list, and if you feel like there is something critical missing, please contact Ron Milam. To access a much more extensive list of relevant reports, tools, and articles about a broad range of intersecting issues, check out our Resources page.

